Exploring Advanced Industrial Compressor Components
Moving Past Basic Compressor Knowledge
Compressors power countless industrial processes. When you move beyond basic components, you unlock efficiency, dependability, and innovation. This blog unveils cutting-edge parts shaping today’s industrial compressor landscape.
Understanding Compressor Specifications
Specifications like pressure, flow, and type determine compatible components. Misreading them causes performance problems and costly repairs. Advanced specs include speed variation and cooling methods, impacting parts and maintenance. Accurate specs guarantee optimal part selection.
Understanding ‘The Types’ First
- Rotary Screw Compressors
They use twin helical screws to compress gas smoothly and continuously. These compressors excel in heavy industry with fewer moving parts and lower noise. Cooling options vary between oil and water systems. Power ranges typically from 3 to over 1,200 horsepower. Precision machining reduces leakage losses. - Reciprocating (Piston) Compressors
These use pistons to compress gas in alternating pulses, ideal for short-term high-pressure bursts. They are lightweight, portable, and cost-effective, commonly used in small factories and workshops. Multi-stage designs boost pressure capacity. They tend to be noisy and require regular wear monitoring. Perfect for variable demand operations. - Centrifugal Compressors
They compress gas using impellers, converting velocity into pressure through diffusers. Industries like petrochemicals use them for high-capacity, continuous duty. They remain efficient under partial loads and are lighter than piston models. High precision CNC machining and skilled operators are essential. - Axial Compressors
These compress gas via multiple rows of rotating and fixed blades. They suit very high airflow rates, such as jet engines and power plants. They achieve about 90% efficiency but involve complexity and high costs. Mostly custom-built for specific applications. - Rotary Vane and Scroll Compressors
Rotary vane compressors use sliding blades for quiet, efficient operation under medium pressure. Scroll compressors contain two interleaved spiral components for smooth and silent compression. Both types serve sensitive environments like electronics and pharmaceuticals due to reliability and cleanliness.
Looking At Rising Trends
Advanced Materials and Coatings
Manufacturers use high-strength composites and alloys to extend component life and resist heat. Specialized coatings reduce wear and corrosion—vital in tough industrial settings. While pricier initially, these materials cut downtime and lengthen replacement intervals.
Manufacturers use high-strength composites and alloys to extend component life and resist heat. Specialized coatings reduce wear and corrosion—vital in tough industrial settings. While pricier initially, these materials cut downtime and lengthen replacement intervals.
Smart Monitoring and Compatibility Assurance
Built-in sensors monitor critical parameters for proactive maintenance and efficient performance. Suppliers test components against specifications to ensure precision compatibility. Reliable, spec-matched parts reduce failure risks.
Built-in sensors monitor critical parameters for proactive maintenance and efficient performance. Suppliers test components against specifications to ensure precision compatibility. Reliable, spec-matched parts reduce failure risks.
Critical Advanced Components
- Variable Speed Drives (VSD)
VSDs adjust motor speed according to compressor demand, boosting energy efficiency. They can cut industrial energy use by up to 20%. New water-cooled VSDs dissipate heat better. However, many plants still use fixed-speed drives, sparking debate about upgrade timing. - Smart Monitoring Systems
Inline sensors track pressure, temperature, and usage in real time. IoT-enabled systems enable predictive maintenance to prevent failures. From 2025, most new compressors will include these smart features, significantly reducing downtime. - Advanced Materials
Special alloys and composites form the backbone of durable, heat-resistant components. Users often debate the trade-off between higher cost and longer lifespan. - Oil-Free Compressor Parts
Oil contamination is unacceptable in food, pharma, and electronics sectors. Oil-free systems use seals and piston coatings to prevent contamination. Demand grows with stricter quality and sustainability standards. Industrial sales of oil-free compressors are rising at about 6.3% annually. - E-Compressor Technology
Electric compressors, independent of engines, gain rapid adoption, especially in the automotive field. The e-compressor market will nearly double from $2.5 billion in 2025 to $5.8 billion by 2035. They reduce emissions but require balancing costs and integration challenges. - Advanced Filtration Systems
HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) and particulate filters deliver clean compressed air. Sensitive processes and longer equipment life depend on effective filtration. Industries increasingly mandate these filters to ensure compliance and efficiency. - Precision Engineering & CAD Designs
CAD and finite element analysis refine component aerodynamics and strength. This leads to quieter, more efficient compressors with extended service life. Suppliers with precision-engineered parts gain a competitive edge.
Getting the Right Spare Parts: Where Reliability Matters
Handling specs, compatibility, and tech complexities demands trusted suppliers. K-Nine Spares (k9spares.com) stands out by providing OEM-quality, compressor-specific components. They focus on:
- Strict specification matching to avoid errors
- Thorough compatibility testing for complex components
- Sourcing from high-quality manufacturers offering warranties
- Sharing maintenance tips and predictive replacement advice
Partnering with suppliers like K-Nine ensures parts meet standards and perform reliably, lowering operational risks.
You may also want to know about “Industrial Compressor Predictive Maintenance”Read here
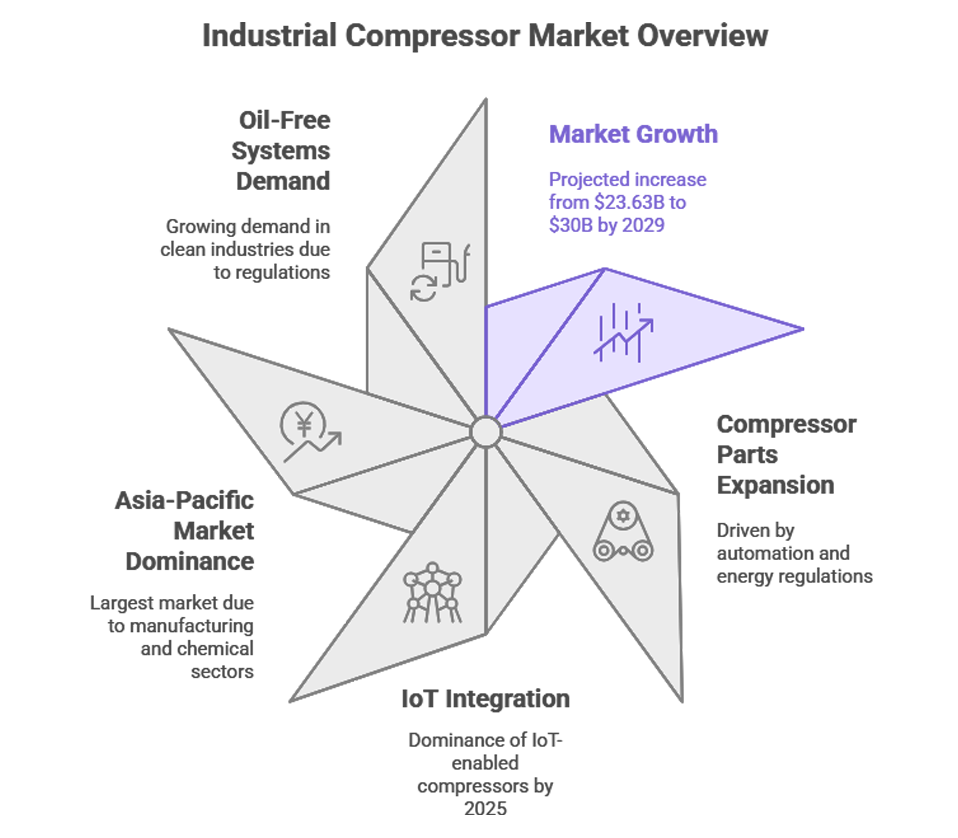
Major Industry Trends and Statistics
- The global industrial compressor market will grow from $23.63 billion in 2025 to nearly $30 billion by 2029.
- The compressor parts market is rapidly rising due to automation and stricter energy policies.
- IoT-enabled compressors will become standard, with most systems integrated.
- Asia-Pacific leads the global compressor components market, fuelled by manufacturing and chemical sector growth.
- Oil-free compressors dominate in food, pharma, electronics, and clean industries, driven by regulations and sustainability.
Debates and Differing Perspectives
Cost over time shapes spares selection debates. New technology and materials raise upfront costs but reduce breakdown frequency and expenses. Some delay upgrades, fearing budget impacts, risking outdated, inefficient setups. Another divide exists between oil-free and conventionally lubricated compressors, balancing contamination risk against cost and operational familiarity.
Smart Summary
- Advanced compressors feature VSDs, smart sensors, and durable materials.
- IoT tracking cuts downtime and enables predictive maintenance.
- Oil-free compressors are essential for contamination-sensitive industries.
- E-compressors are rapidly growing, especially in the automotive sector.
- Precision engineering enhances efficiency, lifespan, and noise control.
- Trusted suppliers like K-Nine Spares provide high-quality, compatible parts.
- Stay ahead by partnering with K-Nine Spares to future-proof your operations.
Your views & insights are most welcome! Leave us a comment below.




