The Compressor Troubleshooting Guide. Diagnosing Common Problems
Introduction:
Welcome to the world of compressors, where perfection hardly exists, pressure is everything, and every minute counts. Downtime for a compressor isn’t just a headache; it’s a ticking clock on your profit and customer promises. This Compressor troubleshooting guide will be of great help.
The industrial compressor market is growing to reach 28.67 billion dollars by 2034 at a growth rate of 4.14% CAGR. That means more machines, more parts, and, quite frankly, more headaches if your troubleshooting game isn’t sharp.
Let’s flip that script. Here is how to diagnose, troubleshoot, and future-proof your compressor operations-straight, with facts, and field-tested advice.
Understanding Your Compressor: Quick Specs 101
Specs matter—think horsepower (engine power), pressure (force per area, usually PSI), and flow (air delivered per minute, often CFM). An incorrectly-sized compressor will cause your air lines to lose pressure, much like a leaky bike tyre that isn’t pumped up enough.
Always check the nameplate from the manufacturer. Match your CFM, PSI, and duty cycle needs. Also, remember each style of compressor has its quirk, be it reciprocating, rotary, or scroll.
Great for food and pharma, the oil-free units are-but be prepared for more noise. The rotary screws own big factories, and the reciprocating love on-off duty cycles. One size never fits all.
Key Components: What really needs your attention
Compressor health begins with the basics. Keep your eye on these:
- Air Intake Filter: Your first line against dust and gunk.
- Relief/Check Valves: A must. Prevent the “whooshing” backflow sneak attacks.
- Oil System For lubricated compressors, poor oil = blown bearings.
- Belts, Couplings & Seals: Cracked rubber here means the silent killer – vibration damage.
- Safety Valves & Sensors: These must never be bypassed. These are your last fail-safes.
- It costs money to ignore those little leaks or dirty filters—maybe the whole compressor.
Common Compressor Problems: And How to Spot Them
Troubleshooting is detective work. Every symptom tells a story.
The compressor does not start.
- Check the power supply first. An unseated plug happens to the best.
- Check if the breakers have tripped; replace fuses if needed.
- Bad pressure switch? Swap it. In lubricated models, check your oil.
Overheating: Why, Oh Why?
Overheating is normally due to either air flow problems, overloading, or poor lube.
- Check for choked air filters, blocked vents, or wrong oil.
- Clogged oil coolers and heat exchangers have caused mysterious shutdowns.
- Low Pressure or Air Delivery
- Leaky pipes are common and expensive.
- Replace dirty filters.
- A failing check valve can make the pressure nosedive fast.
Noisy Operation
- Rattling means loose bolts or dying bearings. Do not ignore the clatter.
- Grinding: Metal-on-metal screeching? Shut down before damage gets catastrophic.
- Unexpected Shutdowns
- Electrical faults, errors of sensors, and automatic protections against overload may occur.
- Always check system panels for error codes.
Actual Industrial Data: What the Statistics Say
The industrial compressor market was valued at USD 19.11 billion in 2024. Among all major markets, the Asia Pacific dominated and had a value of USD 7.89 billion in 2023. There is more and more complexity in compression, as double-stage compression already makes up 48% of the market share.
Rotary compressors account for 31% of sales due to versatility and durability. Within the air compressor parts arena, this market was valued at US$8.5 billion in 2024 and is growing yearly at 4.5%. The numbers in this case mean more units, more tech, and-let’s be honest-more things that can and will break.
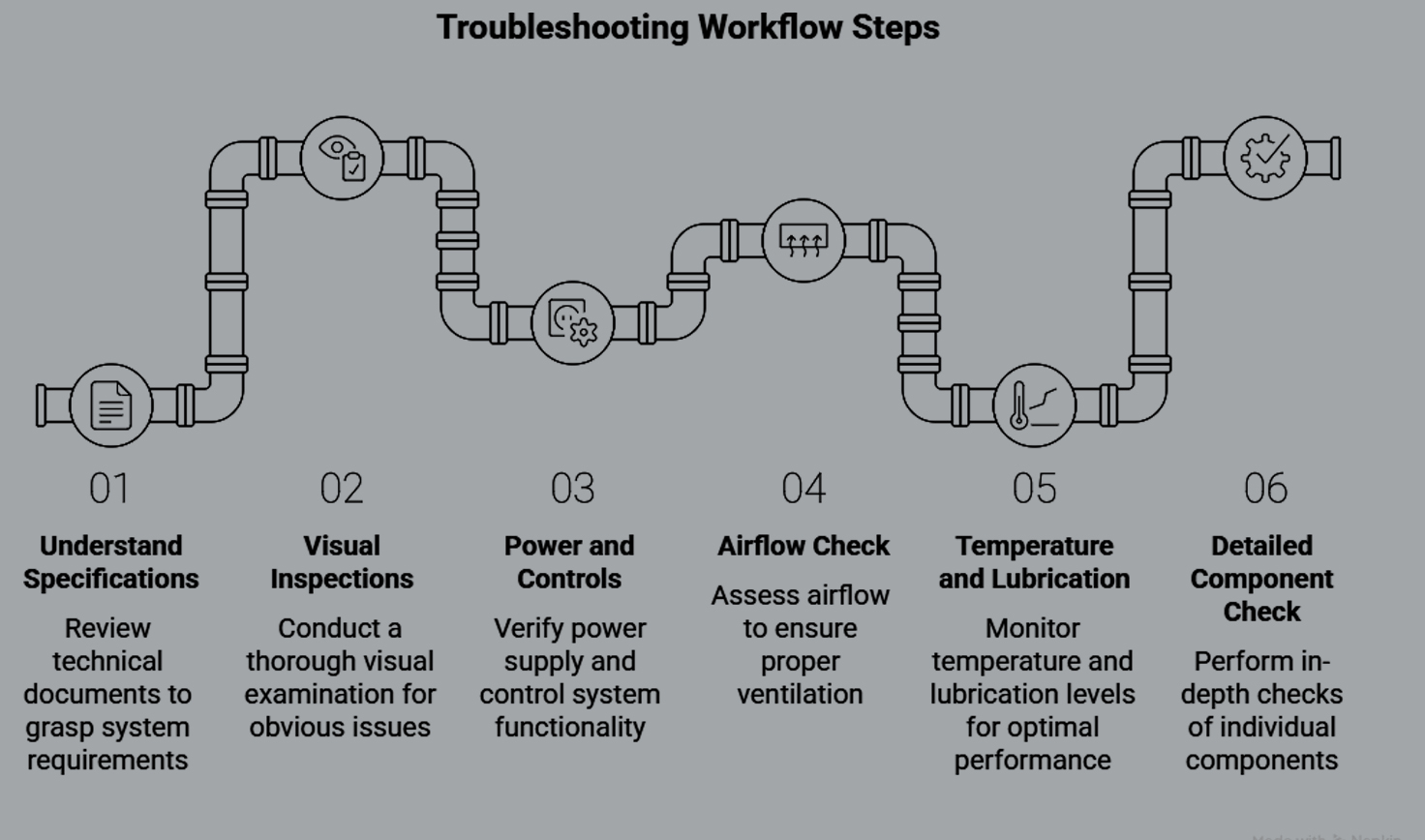
A Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Workflow
It’s like troubleshooting a misbehaving laptop: one eliminates variables, then follows through the order of logic steps one after another without skipping.
Step 1: Understand the Specifications
Do not mix up CFM or PSI requirements: It over-stresses the components, killing efficiency.
Verify compressor nameplate against process requirements.
Step 2: Visual Inspections
Start with the simple things first: check for oil or water leaks, or dust caking.
Are belts, pulleys, and hoses snug and intact? Listen for abnormal sounds.
Step 3: Power and Controls
Check the power input. Ensure breakers, fuses, and overload relays are healthy.
Check sensors and pressure switches. They are often the cheapest failures.
Step 4: Airflow Check
Check intake filters; blockages destroy efficiency.
Test check valves for leaks with soapy water.
Step 5: Temperature and Lubrication
High operating temperatures are usually symptomatic of problems in airflow, coolant, or oil.
Change oil if dark, milky, or low. Any sudden rise in oil consumption means internal wear.
Step 6: Detailed Component Check
Test safety valves, pressure reliefs, and electronic sensors.
Look for data codes or alerts; most compressors today have digital readouts.
Ensuring Compatibility: Mixing and Matching Blindly Doesn’t Work
- Random spare parts cause chaos and void warranties.
- Match OEM part numbers or certified equivalents.
- Inspect materials—for example, seals should match oil type and pressure.
- The Digital twin and barcode systems avoid several costly errors.
- Buy from sources offering full traceability and compliance. Fakes are becoming common, and the risks-think fire or blowouts-are very real.
Sourcing Reliable Parts: Why It’s a Big Deal. Downtime is expensive.
One hour could cost over $10,000+, depending on your industry. The trusted suppliers don’t just sell, they offer technical advice to make sure you get the correct part, first time. Partner with companies that are investing in R&D and fast logistics. Parts availability today is a Top-3 driver for compressor buyers.
Spotlight: K-Nine Spares—Your Parts Powerhouse
K-Nine Spares stands out in this competitive landscape and brings global expertise to local operations.
What differentiates K-Nine Spares is the depth of the catalog for all major OEMs, supplemented by real-time support and industry-standard certifications. Sourcing from K-Nine Spares offers assurance of reliability and clear documentation for every order, thanks to its digital integration and end-to-end traceability. The website of this company, https://k9spares.com/, smooths the procurement process so you get an exact match every time-quicker and more reliably than through old channels.
Forward Thinking: Trends Shaping the Spare Parts Landscape.
The leaders in this industry are changing how inventory is managed. Coming next will be sensor-driven predictive maintenance and blockchain-powered traceability.
AI-driven forecasting slashes downtime up to 40%, while future spare parts will be much more interoperable across brands thanks to modular system designs. And then there’s sustainability: more rigorous adherence to materials and recyclability will continue to push the bar higher for both suppliers and buyers.
Must-Know Troubleshooting Tips (From the Field)
Always start with the basics: power, air, oil, and sensors. Keep a troubleshooting log. Trends show up only when tracked. Never “band-aid” major issues–temporary fixes usually cost more later. They can resolve 85% of issues during the very first visit—provided they follow a detailed, systemized approach.
Conclusion: Shape Your Uptime Future
Compression issues can be resolved with the proper process, partners, and parts. The compressor and parts market will continue to be dynamic and demanding. Adaptability, data-based maintenance, and partnering with suppliers like K-Nine Spares are the modern playbook. Stay sharp. Smart troubleshooting, reliable sourcing, and a proactive mindset are what the future of compressor uptime will be based on.




